https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20260204/index.html
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2026/sc/d5sc09921h
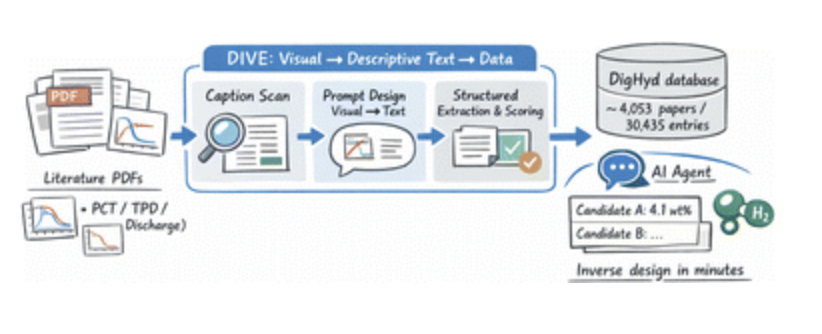
A team from the University of Tokyo and Tohoku University has develop the Descriptive Interpretation of Visual Expression (DIVE) multi-agent workflow, which systematically reads and organizes experimental data from graphical elements in scientific literature.
When applied to solid-state hydrogen storage materials, DIVE markedly improves the accuracy and coverage of data extraction compared to the direct extraction method. Building on a curated database of over 30 000 entries from >4000 publications, a rapid inverse-design AI workflow capable of proposing new materials within minutes was established.