https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-025-01782-2
https://sj.jst.go.jp/news/202601/n0122-02k.html
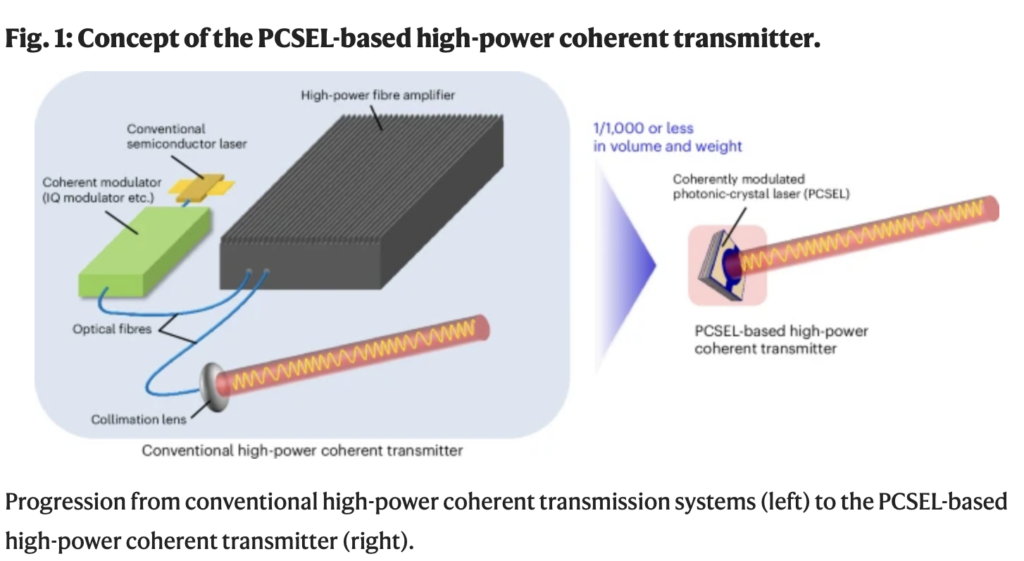
A team from Kyoto University, KDDI and Chitose have developed a laser which can potentially bride the distances of over 380,000 km between earth and moon.
Photonic-crystal lasers normally can only output a fixed frequency. In this study, the researcher developed a photonic-crystal laser that can output lasers of different frequencies on both sides of the photonic crystal by finely adjusting the structure of only half of the photonic crystal, changing the distance between crystal holes by about 0.01%. Through varying the magnitude of current flowing to the left and right, the frequency of the output laser could be adjusted.
In communication experiments simulating propagation loss in space, they demonstrated that communication could be established even when light was attenuated approximately 2 to 3 times stronger than conventional photonic-crystal lasers. This makes intersatellite communication over propagation distances of approximately 60,000 kilometers feasible. By further improvements and enlarging such photonic-crystal devices, space communications over 380,000 kilometers between the Moon and Earth could become possible.